Python
Analyze JSON data using Python (https://vason.io/open-python)
Vason allows you to analyze the JSON content using Python language.
Example: user interface and Jsonata query
import pyjsonata
from vason import LEFT_EDITOR_TO_STRING
# printing to the console
print('Get planet name by index')
# getting content from the user interface
text = LEFT_EDITOR_TO_STRING()
# analyzing by using pyjsonata library
planet = pyjsonata.jsonata('**.planets[position="3"].name', text)
# sending to output
planet
# output: Earth
Example: HTTP request and Jsonata query
import requests
import pyjsonata
# HTTP request
x = requests.get('https://vason.io/examples/exampleGetPlanets')
# analyzing by using pyjsonata library
planet_names = pyjsonata.jsonata("""
**.planets[[0..8]].name[]
""", x.text) # or x.json()
# sending to output
planet_names
# output: array of planets
Vason API
Additionally, there are non-blocking Vason API functions available for sequential execution mode, ensuring operation without blocking the GUI:
-
import vason or from vason import FUNCTION - to use the Vason API, you need to import the vason module.
-
vason.CLEAR_CONSOLE() - clear console
-
vason.CONSOLE(<text or object>) - print text or object on console box
-
vason.ERROR(<error message>) - print error message on console box
-
vason.LEFT_EDITOR_TO_STRING() - return text from the left editor
-
vason.RIGHT_EDITOR_TO_STRING() - return text from the right editor
-
vason.STRING_TO_LEFT_EDITOR(<text>) - write text to the left editor
-
vason.STRING_TO_RIGHT_EDITOR(<text>) - write text to the right editor
-
vason.SET_CURRENT_THEME(<"light"|"dark">) - change current user interface theme
-
vason.GET_CURRENT_THEME() - get current user interface theme name. Return: "light" or "dark"
-
vason.CLEAR_OUTPUT() - clear python output: output box with the DOM element ID = GET_OUTPUT_HTML_ELEMENT_ID()
-
vason.DISPLAY_IN_OUTPUT(<*values>, < target=None >, <append=True>) - This function is capable of introspecting the python object(s) it receives, determining the correct method for displaying them on the webpage.
- *values - a list of values to be displayed
- target - the DOM element where the content should be placed; by default, it's the output box with the DOM element ID = GET_OUTPUT_HTML_ELEMENT_ID()
- append - a flag indicating whether the output will be appended to the target
-
vason.GET_OUTPUT_HTML_ELEMENT_ID() - retrieve the ID of the output DOM element to interact with the user interface using the JavaScript API in Python. See example below:
from js import document
from vason import GET_OUTPUT_HTML_ELEMENT_ID
# get HTML element
outputElement = document.getElementById(GET_OUTPUT_HTML_ELEMENT_ID())
# write text to HTML element
outputElement.innerHTML = 'Test output text'
-
vason.INSTALL_PYTHON_MODULES(<list or item>) - explicit install external python modules
- "module_name" or "module_name==version";
- "wheel URI" - Python wheels are a pre-built binary package format for Python modules and libraries. They are designed to make it easier to install and manage Python packages, by providing a convenient, single-file format that can be downloaded and installed without the need to compile the package from source code. See example below:
from vason import INSTALL_PYTHON_MODULES
INSTALL_PYTHON_MODULES([
'https://cdn.holoviz.org/panel/1.4.1/dist/wheels/bokeh-3.4.0-py3-none-any.whl',
'https://cdn.holoviz.org/panel/1.4.1/dist/wheels/panel-1.4.1-py3-none-any.whl'
])
- vason.LOAD_SCRIPTS_OR_STYLES(<list or item>) - Loading scripts or styles from external sources, or executing a script from text. See examples below:
from vason import LOAD_SCRIPTS_OR_STYLES
LOAD_SCRIPTS_OR_STYLES('https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/font-awesome/6.5.1/css/all.min.css')
LOAD_SCRIPTS_OR_STYLES([
'https://cdn.bokeh.org/bokeh/release/bokeh-3.2.2.min.js',
'Bokeh.set_log_level("info")'
])
User interface
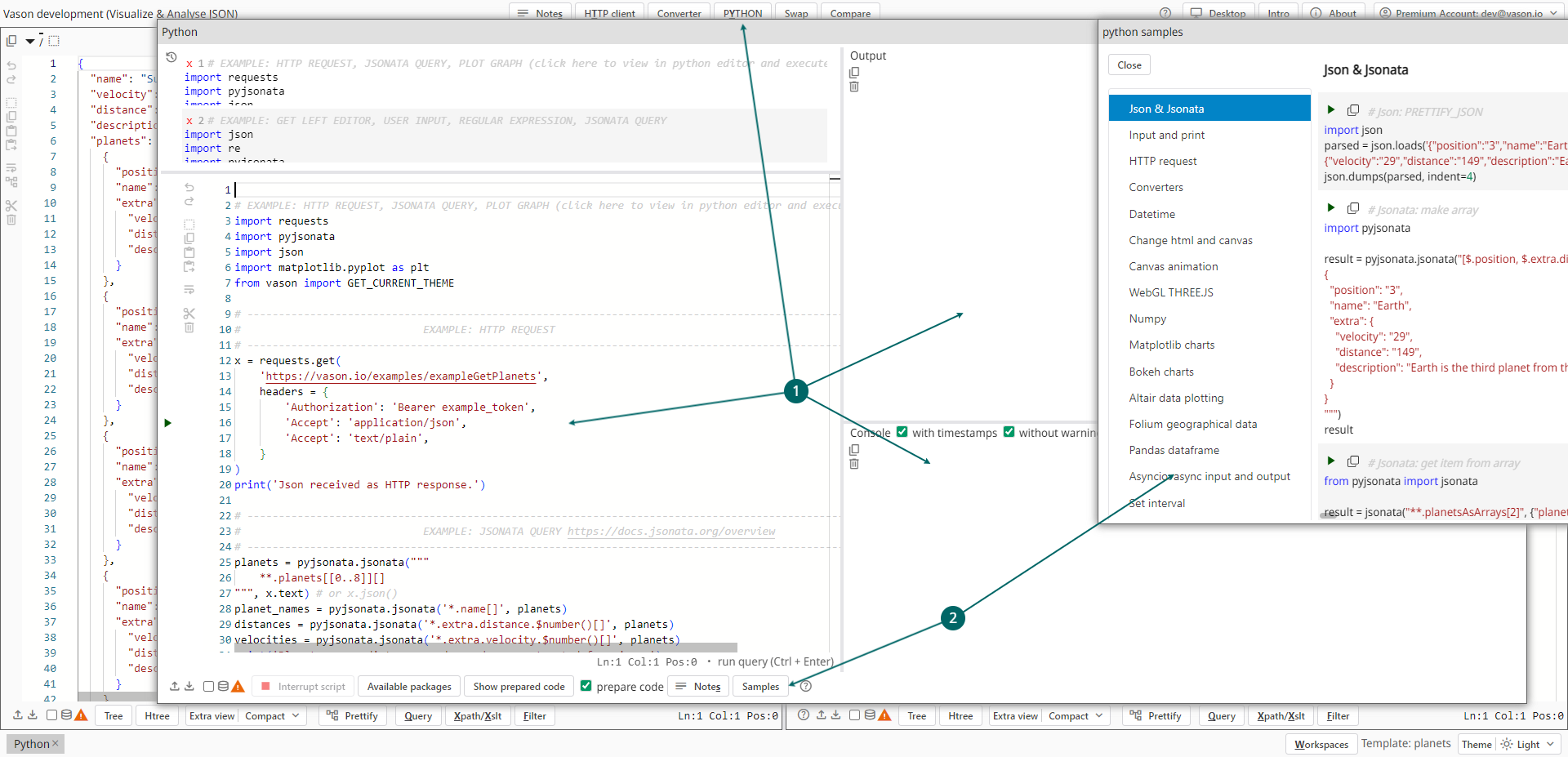
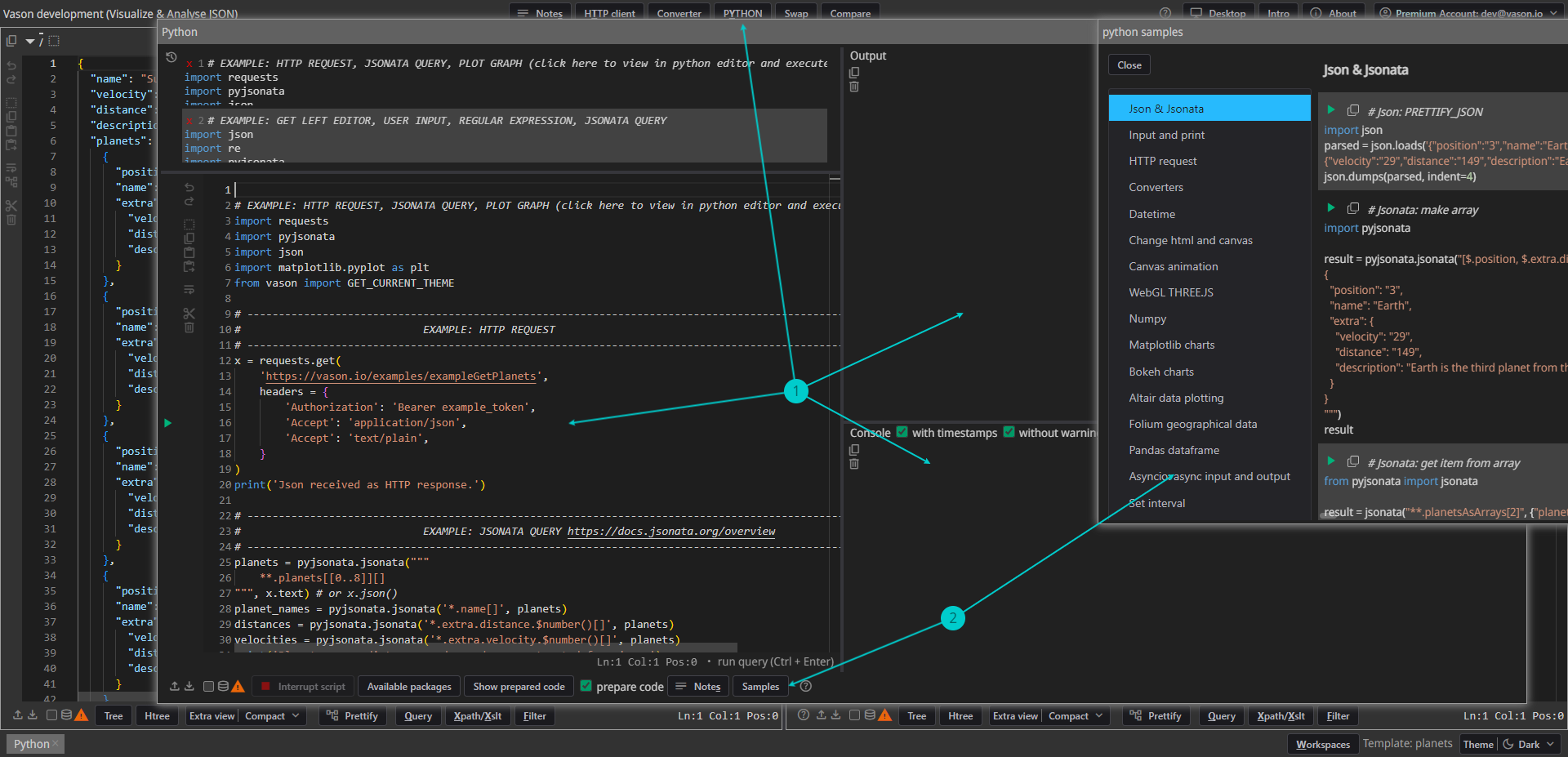
- Utilizing Python:
- Access the
Pythonwindow by clicking thePythonbutton or pressingAlt+Y. - Edit Python scripts in the left section of the
Pythonwindow. - View output (text, JSON, or graphics) in the top right section.
- Observe the console in the bottom right:
- This console serves for intermediate output, such as print('text'),
- or functions as an interactive terminal for user input, e.g.
- Access the
a = input('Enter text: ')
- Explore Python examples in the
Python sampleswindow.